How does Displacement Scale actually work in Blender?
Check the video to see what Displacement node value works best.
More details are in the article below.
Not everyone understands what Displacement is. In simple terms, Displacement is a dent on the surface, as if we were pressing soft clay with the palm of our hand.
So the Displacement Scale is the force with which we press into the clay. However in Blender, we can press not only against the depth of the surface but also to the opposite side.
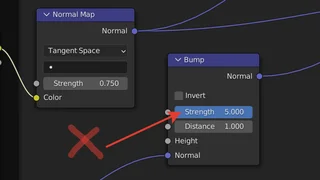
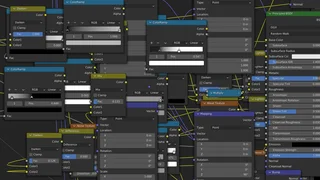
To understand how the Displacement node works, we need to look at some of the material settings.
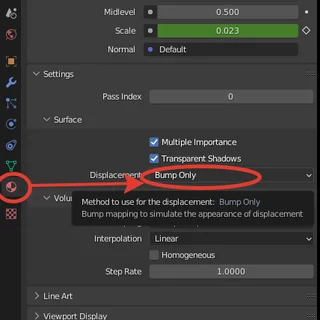
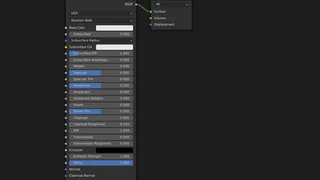
The first method to display Displacement is via "Bump Only".
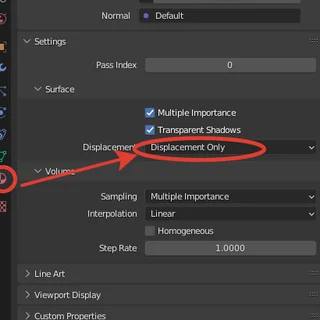
The second method to display Displacement is via "Displacement Only".
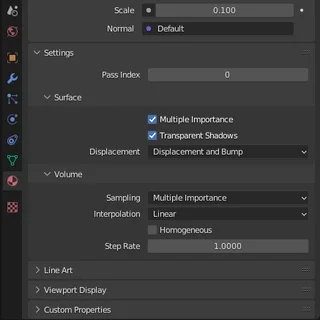
And finally, the last and most resource-consuming method is via "Displacement and Bump".
If we use the "Bump Only" method, there is no actual "extrusion" of the surface. This means that the plane remains plane, but dents and convexities do not appear on it. These changes remain "virtual" and we can see them on the surface only with the help of shadows. Often this is more than enough for a reasonably realistic image. It's the easiest way for the CPU to make calculations because there is no actual change in the geometry and the plane remains plane.
Nevertheless, the Displacement setting is still an important parameter because it determines how accurate the shadows will be and how visible all the irregularities on the surface will be.
It's good to remember that on the Displacement Scale, 1 equals 1 meter of extrusion. In most materials, the surface rarely changes that much. Typically the Displacement Scale ranges from 5 centimeters to a couple of millimeters, that is from 0.05 to 0.001. Below you can see examples of how the shadows change in real-time depending on the Displacement Scale.
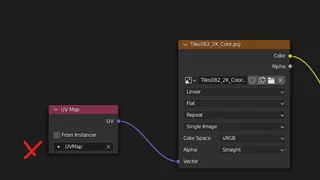
You can find the Displacement node in the Shader Editor
In the example below, you can see how the shadows on the surface change when you change the Displacement Scale from 0 to 0.1 or from 0 centimeters to 1 meter.
Notice how near the end of the animation there is distortion and black dots appear on the surface of the bricks due to excessive Displacement Scale.
Below are more examples of surface visualization with different Displacement Scale from 0.01 (1 centimeter to 1 meter).
- Displacement Scale 0.03 or 3 centimeters - Soft, correct shadows without distortion or artifacts.
- Displacement Scale 0.1 or 10 centimeters - Shadows are harsh, artifacts start to appear.
- Displacement Scale 1 or 1 meter - Shadows are harsh, artifacts and black dots all over the place.
To explain the displacement scale even more clearly, let's turn to the option in the material settings called "Displacement Only".
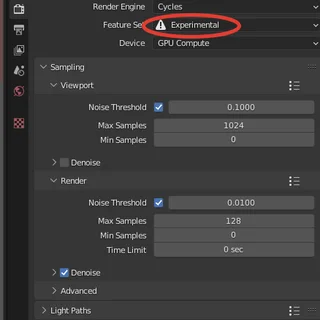
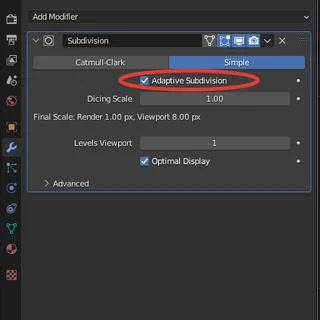
This option is available when certain parameters are activated in the Blender settings.
- You need to set Blender to Experimental mode.
- Then you have to apply the Subdivision surface modifier and activate the "Adaptive Subdivision" option.
In the video examples below, you can see how Displacement Scale works with the Experimental mode, "Adaptive Subdivision" and "Displacement Only".
In this video, you can see how the surface of the material changes as the Displacement Scale increases from 0 to 1 (0 to 1 meter)
So, when you break it down, it's actually simple :) Just imagine how deep the irregularities on the material you are working with should be and set the Displacement Scale according to these values.
Thank you for reading and have a great BlenderKit day!